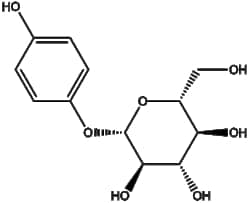
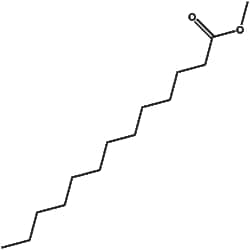
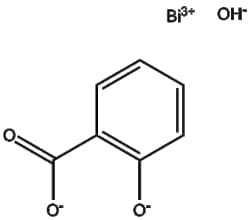
Welcome to fishersci.com
Choose the brand aligned with your industry so we can best serve your needs.

For researchers, scientists, and technical professionals: Your one-stop shop for the complete range of laboratory, production, and safety products and services.
Explore Now
For healthcare professionals: Your proven destination for comprehensive diagnostic and clinical laboratory products and services.
Explore Now